A Survey of Kafka
Table of Contents
:ID: 355A2592-CBDA-4B02-BC9B-9F75F3867C62
# What is it?
See also https://kafka.apache.org/
It’s a distributed event streaming platform.
# General use case
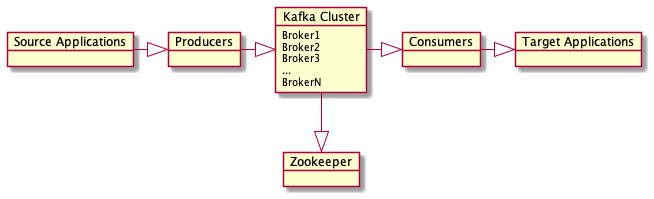
Share data (ie, events, messages, etc) between applications. Producers publish messages and consumers read those messages. See introduction for more details and more specific use cases.
object "Source Applications" as Source
object Producers
object "Kafka Cluster" as Cluster {
Broker1
Broker2
Broker3
...
BrokerN
}
object Zookeeper
object Consumers
object "Target Applications" as Target
Source -r-|> Producers
Producers -r-|> Cluster
Cluster -r-|> Consumers
Cluster -d-|> Zookeeper
Consumers -r-|> Target
A good way to learn how Kafka works is to spin it up locally and use the CLI to create topics, publish and consume messages. See CLI usages below.
See Kafka docker for a super quick way to get up and running locally.
# Concepts
# Topics
- a named message stream
# Partitions
- Topics are split into partitions (message logs)
- Messages for a given topic are placed into partitions
- Messages that have the same key are always placed in the same partition guaranteeing order
- Messages without a key are plopped into partitions round robin
# Producer
- Something that sends messages
# Consumer
- Something that reads messages
- Consumers can define which offset they begin reading from (the beginning of the log, the current position, the last position the consumer read from)
# Groups
- Consumers can be put into groups that consume the same topic. Example: An application can have multiple consumers for a topic. When in a group, Kafka will assign each consumer partitions to read from. This allows parallel reads.
- Can have more consumers than partitions, but extra consumers will only consume if other consumers go down.
# Kafka CLI
# kafka-topics
# Adding a topic
kafka-topics --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic first_topic --create --partitions 3 --replication-factor 1
--replication-factor: how many broker nodes should partitions be replicated to.
Must be <= number of brokers in the cluster.
partitionsare distributed across brokers. One consumer reads from a partition. So, the more partitions, the more consumers; hence horizontal scaling.
# Listing topics
kafka-topics --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --list
# Describe a topic
Provides partition, leader, Isr, and replicas info
kafka-topics --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic first_topic --describe
# Delete a topic
kafka-topics --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic second_topic --delete
# kafka-console-producer
Create messages. This opens a prompt where you can add one or more messages.
Press enter key to add the next message. C-c to exit prompt.
kafka-console-producer --broker-list 127.0.0.1:9092 --topic first_topic --producer-property acks=all
producer-propertyis optional and can be used to add other properties. In this example, setting the acks property.- You can specify a topic that doesn’t exist and it will be created. You’ll get an error the first time a message is posted, but it will recover and succeed after the topic is created and a leader is selected.
# kafka-console-consumer
Starts a consumer of messages created by a producer
kafka-console-consumer --bootstrap-server 127.0.0.1:9092 --topic first_topic
- This starts the consumer listening for new messages.
- Add
--from-beginningto consume all the messages and continue to listen for new ones.
# Groups (--group flag)
- Consumers are should usually be grouped by an arbitrary ID.
- Messages are consumed by group members from specific partitions (ie, a single consumer in a group doesn’t read all the messages unless it is the only consumer).
- Messages are read once by consumers in a group (ie, consumer group offsets is what keeps track of messages already consumed by a group)
When a grouped consumer is started, unread messages created before it was started are consumed.
kafka-console-consumer --bootstrap-server 127.0.0.1:9092 --topic first_topic --group app-foo
# kafka-consumer-groups
Use this to list, describe, delete groups. Also reset consumer group offsets
# List groups
kafka-consumer-groups --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --list
# Describe a group
This will give you info about where the consumers are in consuming messages (ie consumer offsets, lag, etc)
kafka-consumer-groups --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --describe --group app-foo
# Reset offsets
There’s a bunch of different options for where to reset the offset to. Here’s
one example using --to-earliest.
kafka-consumer-groups --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --group app-foo --topic first_topic --reset-offsets --to-earliest --execute
# Ruby
See also this Zendesk post for a nice breakdown of the differences between these libraries.